- Mitigation title
- Short rotation coppice
-
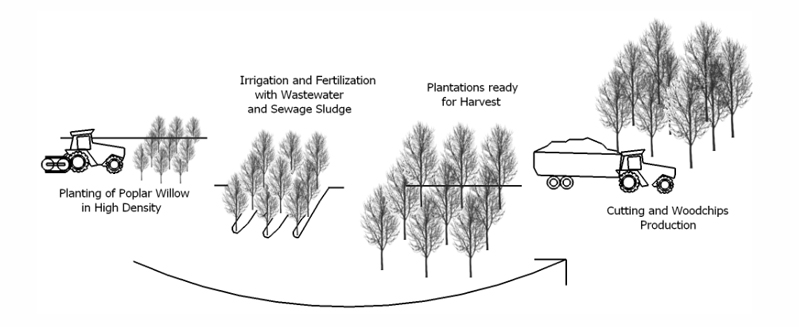
- Description
-
Similar to the wetlands based on willow growth, Short Rotation Coppice (SRC) is usually used for the production of energy crops. It’s a well-established practice and is considered a traditional method for woodland management. It also has the potential to be used to remove excess phosphate, either by being planted in phosphate enriched soils/as riparian buffers, or in a close-loop system similar to wetlands to treat sewage sludge.
- Advantages
-
- Biodiversity enhancement
- Carbon sequestration
- Flood mitigation
- Supports pollination
- Disadvantages
-
- Impacted by climate conditions
- Biomass has to be removed
- Parameters
-
- Phosphorus
- Ammonia
- Nitrogen
- BOD/COD
- Suspended solids
- Carbon footprint
-
- Acts as a net carbon sink
- Time to become effective
-
- Removal of nutrients/organic matter will first need vegetation to become established
- Maintenance
-
- Biomass harvesting is essential. Harvesting needs to be completed every 2-4 years
- SRC plantations may only remain productive for 30 years, after which they may need to be replaced
- Performance with time
-
- Initial performance will be poor but will increase as vegetation grows
- Performance can be kept at optimum with well a well-established maintenance schedule
- Performance fluctuates with seasonal changes; lower in autumn/winter, highest in spring/summer
- Performance fluctuates dependent on growing season
- Scaling considerations
-
The size of the scheme is correlated to the load of nutrient removal, but often requires large land areas to be an effective site. Design criteria to meet:
- Monitoring required of the concentrations and a Population Equivalent must be evidenced
- Mass loading will directly impact sizing, aspect ratio, and depth
- Must take into account climate factors and climate change, such as droughts and dry weather, or water gains from rainfall etc. as well seasonal dynamics and differences in flows through different seasons
- Must take into account seasonal efficiency tied to plant growth
- References
-
Forest Research. (n.d.). Short rotation coppice. Retrieved from https://www.forestresearch.gov.uk/tools-and-resources/fthr/biomass-energy-resources/fuel/energy-crops-3/short-rotation-coppice/
Hänel, M.; Istenič, D.; Brix, H.; Arias, C.A. (2022). Wastewater-Fertigated Short-Rotation Coppice, a Combined Scheme of Wastewater Treatment and Biomass Production: A State-of-the-Art Review. Forest.
Ricardo for Herefordshire Council. (2021). Interim Phosphate Delivery Plan Stage 2, Mitigation options for phosphate removal in the Wye Catchment.
Simon Amiot, A. J.-T. (2020). Optimization of the wastewater treatment capacity of a short rotation willow coppice vegetation filter. Ecological Engineering.
SSWM. (n.d.). Short Rotation Coppice. Retrieved from https://sswm.info/step-nawatech/module-1-nawatech-basics/appropriate-technologies-0/short-rotation-coppice
Xavier Lachapelle-T., M. L. (2019). Treatment and valorization of a primary municipal wastewater by a short rotation willow coppice vegetation filter. Ecological Engineering
